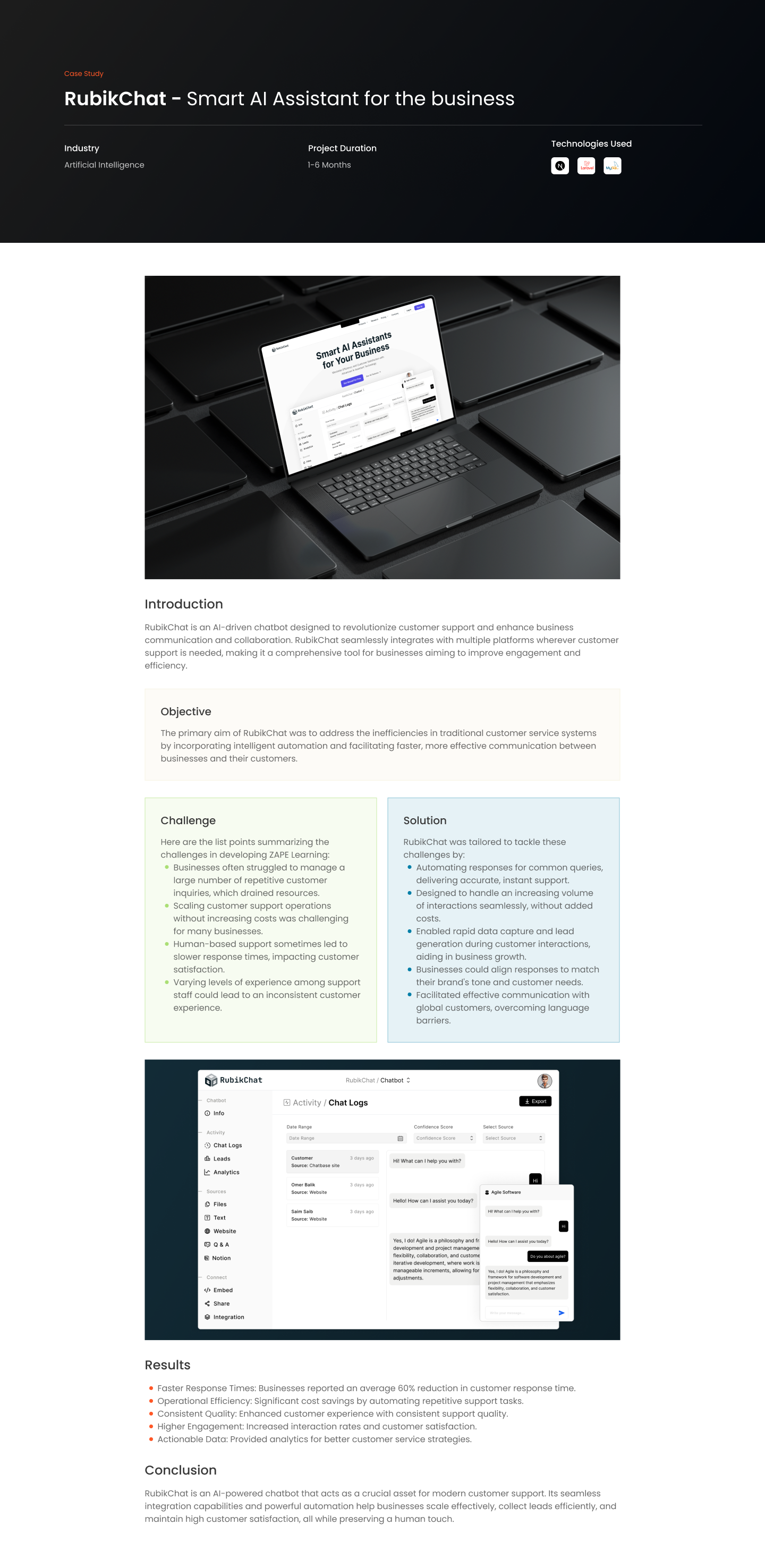
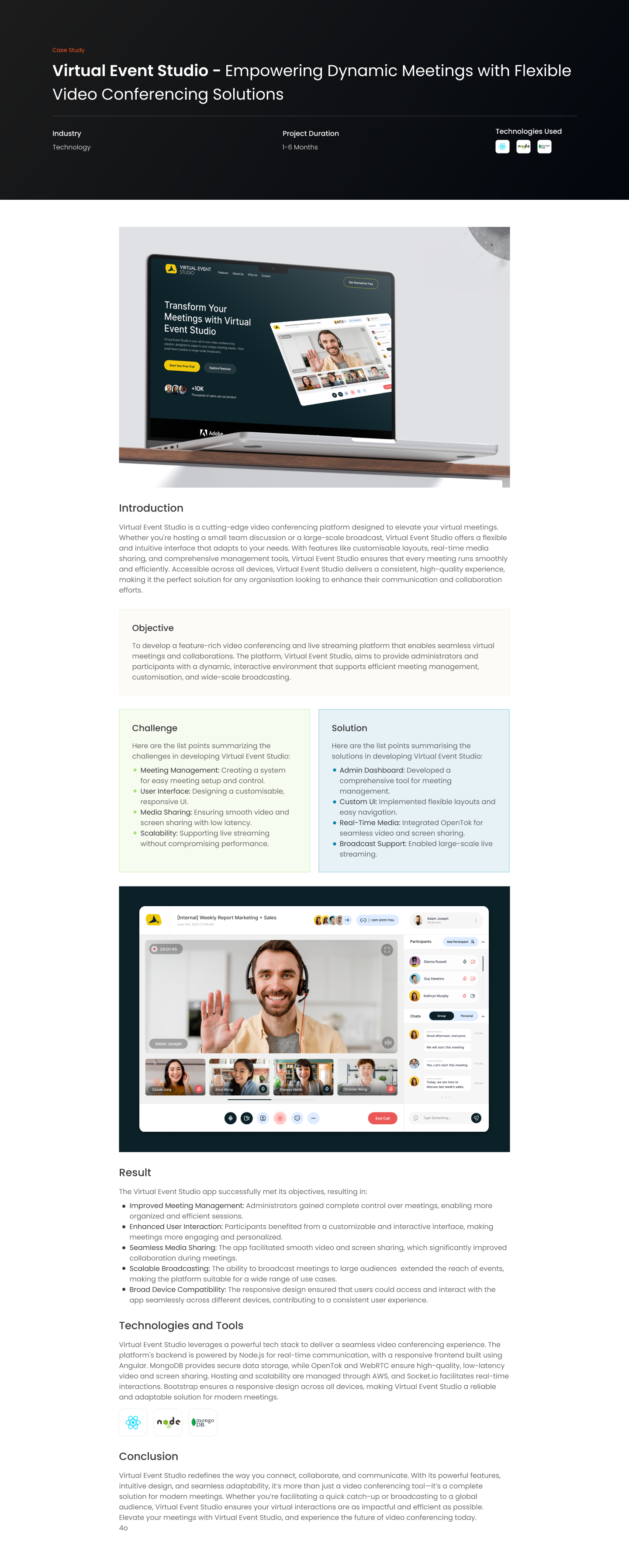
Introduction
Internet of Things (IoT)—where everyday objects are connected to the internet, enabling them to send and receive data. This technology is not just a futuristic concept—it’s here, and it’s reshaping everything from homes to industries. Let’s explore how IoT is revolutionizing our world and what it holds for the future.
What is the Internet of Things (IoT)?
The Internet of Things refers to the network of physical objects—’things’—embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies for the purpose of connecting and exchanging data with other devices and systems over the internet. These ‘smart’ devices range from ordinary household items to sophisticated industrial tools.
Core Components of IoT
1. Sensors/Devices::Collect data from their environment. This could be as simple as a temperature reading or as complex as a full video feed
2. Connectivity:: Devices need to be connected to a cloud infrastructure to send and receive data.
3. Data Processing:: Software processes the collected data and makes decisions based on the data.
4. User Interface:: The end-user interacts with the devices or gets notifications about the IoT system.
Benefits of IoT
1. Efficiency and Productivity: Enhances business processes with data-driven decision-making.
2. Real-Time Monitoring: Offers up-to-the-minute monitoring and data analysis.
3. Automation and Control: : Enables automation of everyday tasks and processes.
4. Enhanced Data Collection: Provides a richer, more accurate dataset for analysis.
5. Cost Savings: : Optimizes resource usage and reduces operational costs.
Challenges and Considerations
1. Security Risks: Increased connectivity brings the risk of data breaches.
2. Privacy Concerns: Handling and protecting the personal data collected by IoT devices.
3. Integration and Compatibility: Ensuring different devices and systems can work together seamlessly.
4. Data Overload and Management: Managing the vast amounts of data generated by IoT devices.
Implementing IoT
1. Smart Homes: From smart thermostats to voice assistants, IoT is enhancing home convenience and security.
2. Healthcare: Wearable devices for monitoring health and telemedicine.
3. Manufacturing: IoT drives smart manufacturing practices with real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance.
4. Agriculture: Sensors for monitoring soil moisture and crop growth to optimize farming practices.
Conclusion
The Internet of Things is rapidly becoming an integral part of our lives, weaving together the fabric of our physical and digital worlds. IoT is not just connecting devices; it’s about connecting people, improving quality of life, and opening up new possibilities for innovation. The future is indeed IoT-driven, and it’s only going to get more interconnected.
Further Reading and Exploration
For readers seeking to deepen their understanding of the Internet of Things (IoT) and explore its vast potential, the following areas offer rich opportunities for learning and engagement:
1. Advanced IoT Technologies: Delve into emerging technologies in IoT, such as edge computing, IoT platforms, and 5G connectivity, and how they are shaping the future of IoT.
2. IoT in Various Industries: Explore how IoT is being applied in different sectors like smart cities, automotive, retail, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and more, including case studies and success stories.
3. IoT Security and Privacy: Understand the challenges and strategies for securing IoT devices and networks, and learn about privacy concerns and best practices in IoT data handling.
4. Building IoT Solutions: Dive into the technical aspects of developing IoT solutions, including sensor integration, data analytics, and cloud computing.
5. IoT Standards and Protocols: Familiarize yourself with the standards and communication
protocols used in IoT, like MQTT, CoAP, and Zigbee.
Each of these topics offers an avenue for a more nuanced understanding of IoT, helping you to appreciate its complexities and vast applications.