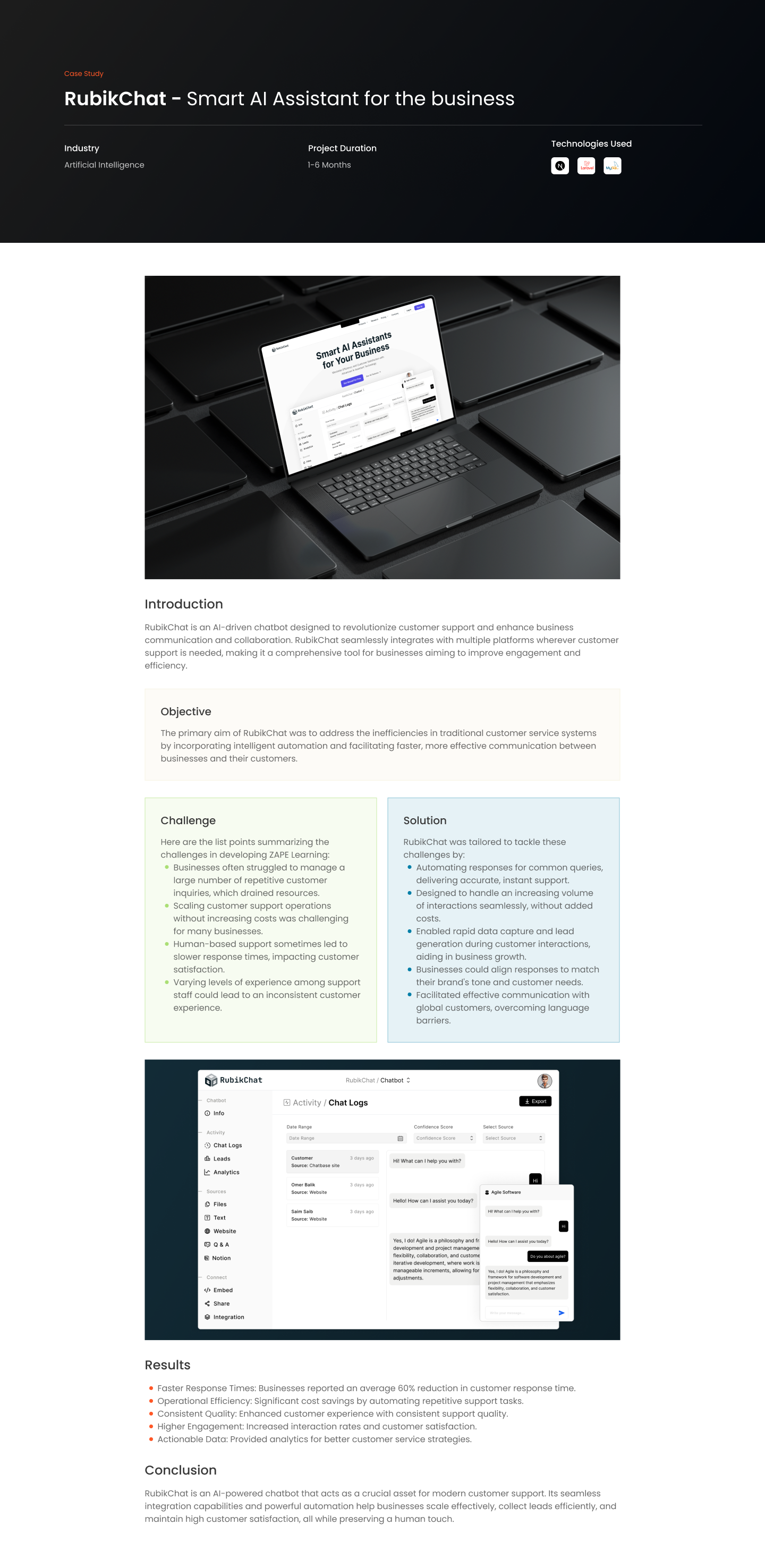
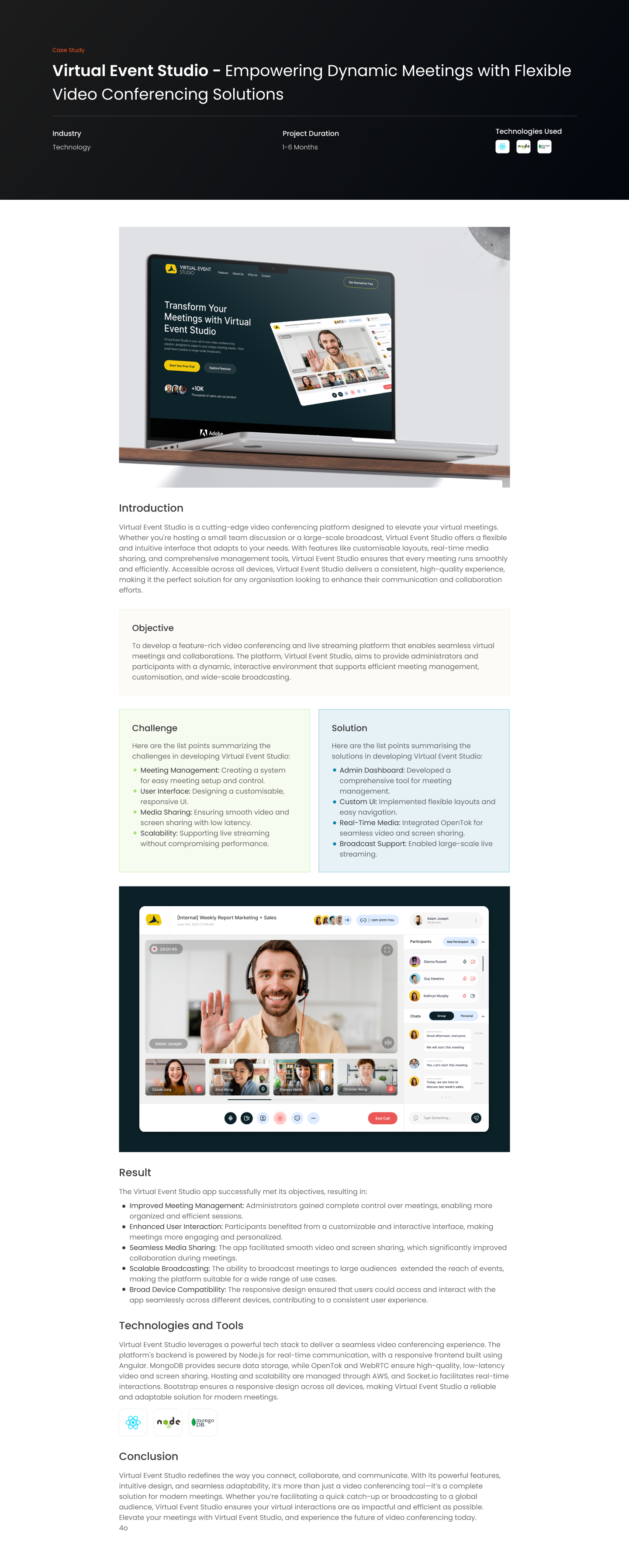
Introduction
This blog will demystify Big Data, explore its immense potential, and examine how it’s transforming industries and shaping our future. Whether you’re a data enthusiast, a business professional, or just curious about the buzz around Big Data, this exploration will provide valuable insights into this ever evolving field.
What is BigData?
Big Data refers to the enormous volumes of data generated every second from various sources like social media, sensors, digital processes, and business transactions. It’s not just the volume of data that’s important but also its variety, velocity, and the value it offers.
Core Characteristics of Big Data
1. Volume: The sheer amount of data generated and stored.
2. Velocity: The rapid rate at which data is produced and processed.
3. Variety: The different types of data, structured and unstructured, like text, images, and videos.
4. Veracity: The quality and accuracy of the data.
5. Value: The actionable insights and decisions that can be derived from the data.
Applications of Big Data
1. Business Intelligence: Provides deep insights into customer behavior, market trends, and operational efficiency.
2. Healthcare: Enhances patient care through predictive analytics and personalized medicine.
3. Smart Cities: Optimizes various aspects of urban living, from traffic management to energy use.
4. E-commerce: Tailors customer experiences through personalized recommendations.
5. Financial Services: Detects fraud and manages risk through real-time analytics.
Benefits of Big Data
1. Informed Decision-Making: Empowers organizations to make data-driven decisions.
2. Operational Efficiency: Optimizes business processes and reduces costs.
3. Innovation: Drives new products and services, fostering innovation across industries.
4. Customer Insights: Enhances understanding of customer preferences and behaviors.
5. Risk Management: Helps in predicting and mitigating potential risks.
Challenges in Big Data
1. Data Quality and Management: Ensuring the accuracy and accessibility of large datasets.
2. Privacy and Security: Protecting sensitive data from breaches and unauthorized access.
3. Integrating Diverse Data Sources: Combining data from varied sources into a cohesive and functional dataset.
4. Skilled Personnel: The need for skilled professionals in data analytics and management.
Big Data Technologies
Key technologies enabling the handling and analysis of Big Data include Hadoop, Spark, NoSQL databases, machine learning algorithms, and cloud computing platforms.
Conclusion
Big Data is not just a trend; it’s a fundamental aspect of how modern organizations operate and compete. Its ability to transform vast, diverse data sets into meaningful insights makes it invaluable.
Further Reading and Exploration
For those eager to dive deeper into the world of Big Data and enhance their understanding, the following topics are highly recommended:
1. Data Analytics Techniques: Explore various data analytics methods and tools that are essential in interpreting Big Data, including predictive analytics, machine learning, and statistical modeling.
2. Big Data Technologies in Depth: Delve into specific technologies like Apache Hadoop, Spark, and NoSQL databases, understanding their architectures, functionalities, and applications.
3. Big Data in Specific Industries: Study how Big Data is being used in different sectors such as healthcare, finance, retail, and telecommunications to gain insights into its diverse applications.
4. Ethics and Privacy in Big Data: Understand the ethical considerations, privacy concerns, and regulatory challenges involved in handling Big Data.
5. Emerging Trends in Big Data: Keep up with the latest trends and advancements in Big Data, such as real-time analytics, the Internet of Things (IoT) integration, and artificial intelligence (AI) driven analytics.
Each of these areas provides a pathway to a more nuanced understanding of Big Data, allowing you to appreciate its complexities and immense potential.